Okay, here’s a comprehensive article about insurance, exceeding 2500 words. I’ve aimed for clarity, depth, and broad coverage of the topic.
Insurance: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Managing Risk
Insurance is a cornerstone of modern financial planning and risk management. It provides a financial safety net, protecting individuals, families, and businesses from potentially devastating losses resulting from unforeseen events. In its simplest form, insurance is a contract, known as a policy, between an individual or entity (the policyholder) and an insurance company (the insurer). The policyholder pays a premium, and in exchange, the insurer agrees to compensate the policyholder for specific losses covered by the policy. This article delves into the intricacies of insurance, exploring its fundamental principles, various types, benefits, and considerations for choosing the right coverage.
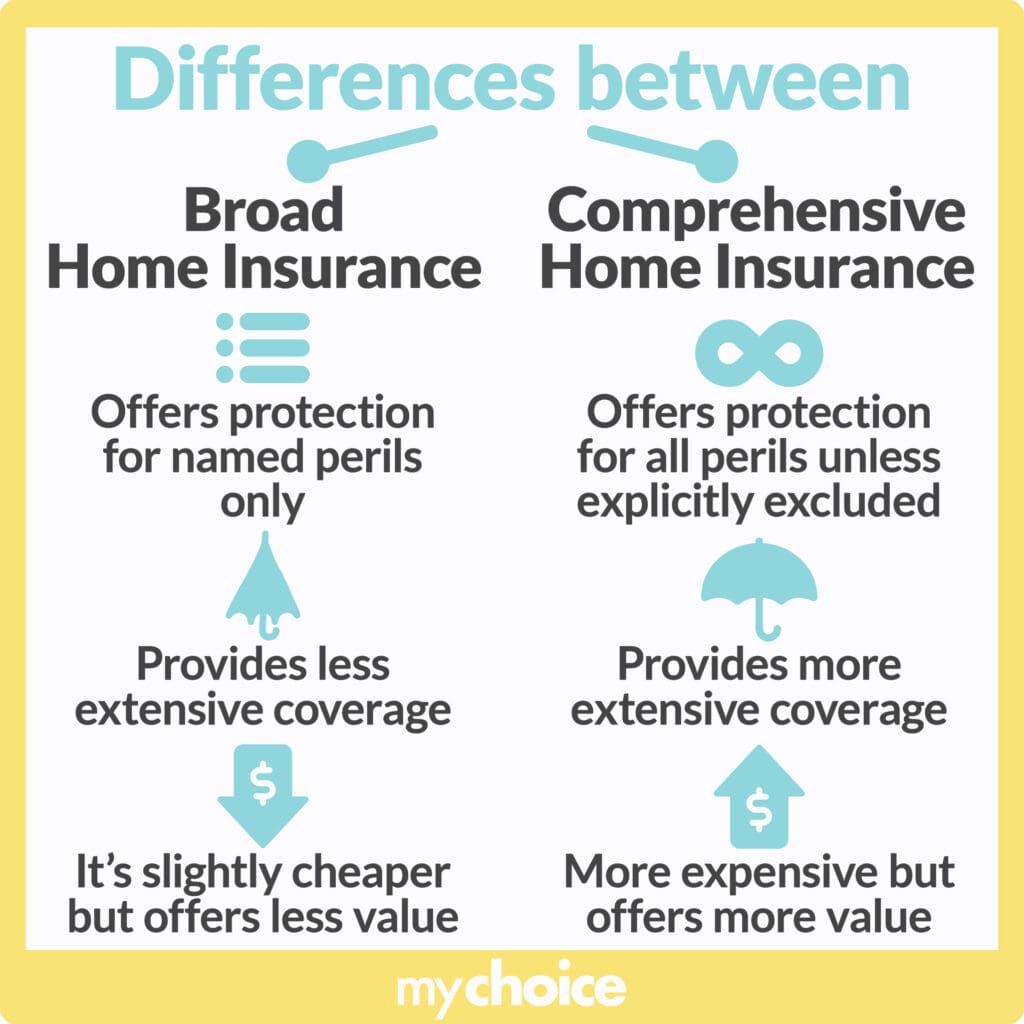
The Core Principles of Insurance
Several core principles underpin the concept of insurance, ensuring its viability and fairness:
-
Insurable Interest: This principle dictates that the policyholder must have a legitimate financial interest in the subject matter being insured. In other words, the policyholder must stand to suffer a financial loss if the insured event occurs. For example, you can insure your own home because you would suffer a financial loss if it were damaged or destroyed. You generally cannot insure your neighbor’s home because you have no financial interest in it. This prevents wagering and moral hazard.
-
Utmost Good Faith (Uberrimae Fidei): Both the insurer and the policyholder have a duty to act honestly and transparently. The policyholder must disclose all material facts that could influence the insurer’s decision to issue the policy or the terms of the policy. The insurer must also be transparent about the policy’s coverage, exclusions, and limitations. Failure to uphold this principle can lead to the policy being voided.
-
Indemnity: The principle of indemnity aims to restore the policyholder to the same financial position they were in before the loss occurred. Insurance is not intended to be a source of profit. For example, if your car is damaged in an accident, your auto insurance policy will typically cover the cost of repairs or the actual cash value of the car, but not more than that. There are exceptions, such as life insurance, which pays out a predetermined sum upon death, regardless of the financial loss.
-
Contribution: If a policyholder has multiple insurance policies covering the same risk, the principle of contribution dictates that the insurers will share the loss proportionally. This prevents the policyholder from receiving more than the actual loss.
-
Subrogation: After an insurer pays a claim, they may have the right to pursue legal action against a third party who caused the loss. This is known as subrogation. For example, if your car is damaged in an accident caused by another driver, your insurance company may pay for the repairs and then pursue the other driver’s insurance company to recover the costs.
-
Proximate Cause: This principle establishes a direct causal link between the insured event and the resulting loss. The loss must be a direct consequence of the insured peril. For example, if a fire damages your home, the fire is the proximate cause of the damage. However, if a flood occurs after the fire, the flood damage may not be covered if flood damage is excluded from the policy.
Types of Insurance
Insurance is a broad category encompassing various types of coverage, each designed to protect against specific risks. Here are some of the most common types of insurance:
-
Life Insurance: Life insurance provides a financial benefit to designated beneficiaries upon the death of the insured. It can help replace lost income, cover funeral expenses, pay off debts, and provide financial security for loved ones. There are several types of life insurance, including:
- Term Life Insurance: Provides coverage for a specific period (e.g., 10, 20, or 30 years). It’s generally more affordable than permanent life insurance but does not build cash value.
- Whole Life Insurance: Provides lifelong coverage and builds cash value over time. Premiums are typically higher than term life insurance.
- Universal Life Insurance: Offers more flexibility than whole life insurance, allowing policyholders to adjust premiums and death benefits within certain limits. It also builds cash value.
- Variable Life Insurance: Combines life insurance coverage with investment options. The cash value fluctuates based on the performance of the underlying investments.
-
Health Insurance: Health insurance helps cover the costs of medical care, including doctor visits, hospital stays, prescription drugs, and other healthcare services. It’s essential for protecting against the potentially high costs of medical treatment. Common types of health insurance include:
- Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs): Typically require members to choose a primary care physician (PCP) who coordinates their care. Referrals are usually needed to see specialists.
- Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs): Allow members to see any doctor or specialist without a referral, but costs are generally lower when using in-network providers.
- Exclusive Provider Organizations (EPOs): Similar to PPOs, but members are only covered for services received from providers within the EPO network.
- Point of Service (POS) Plans: Combine features of HMOs and PPOs. Members can choose to see an in-network PCP or go directly to an out-of-network provider, but costs are higher for out-of-network care.
-
Auto Insurance: Auto insurance protects against financial losses resulting from car accidents, theft, or damage to your vehicle. Most states require drivers to carry minimum levels of auto insurance. Common types of auto insurance coverage include:
- Liability Coverage: Covers damages and injuries you cause to others in an accident.
- Collision Coverage: Covers damage to your vehicle resulting from a collision with another vehicle or object.
- Comprehensive Coverage: Covers damage to your vehicle from events other than collisions, such as theft, vandalism, fire, or natural disasters.
- Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage: Covers your injuries and damages if you’re hit by an uninsured or underinsured driver.
- Personal Injury Protection (PIP): Covers your medical expenses and lost wages, regardless of who is at fault in an accident. (Not available in all states.)
-
Homeowners Insurance: Homeowners insurance protects your home and belongings against damage from events such as fire, wind, theft, and vandalism. It also provides liability coverage if someone is injured on your property.
-
Renters Insurance: Renters insurance protects your personal belongings against damage or theft while you’re renting a home or apartment. It also provides liability coverage.
-
Disability Insurance: Disability insurance replaces a portion of your income if you become disabled and unable to work. It can be either short-term or long-term.
-
Long-Term Care Insurance: Long-term care insurance helps cover the costs of long-term care services, such as nursing home care, assisted living, or home healthcare.
-
Business Insurance: Business insurance protects businesses from a wide range of risks, including property damage, liability claims, and business interruption. Common types of business insurance include:
- General Liability Insurance: Covers bodily injury and property damage caused by your business operations.
- Commercial Property Insurance: Covers damage to your business property, such as buildings, equipment, and inventory.
- Workers’ Compensation Insurance: Covers medical expenses and lost wages for employees who are injured on the job.
- Professional Liability Insurance (Errors and Omissions Insurance): Protects professionals against liability claims arising from errors or omissions in their professional services.
- Business Interruption Insurance: Covers lost income and expenses if your business is temporarily shut down due to a covered event.
Benefits of Insurance
Insurance offers numerous benefits, providing individuals and businesses with financial security and peace of mind:
-
Financial Protection: The primary benefit of insurance is financial protection against unexpected losses. It can prevent financial ruin by covering costs that would otherwise be unaffordable.
-
Peace of Mind: Knowing that you’re protected by insurance can provide peace of mind, reducing stress and anxiety about potential risks.
-
Risk Management: Insurance is a key component of risk management, allowing individuals and businesses to transfer risk to an insurance company.
-
Legal Compliance: Certain types of insurance, such as auto insurance and workers’ compensation insurance, are often required by law.
-
Business Continuity: Business insurance can help businesses recover quickly from disasters and continue operating.
-
Investment Opportunities: Some types of insurance, such as whole life insurance and variable life insurance, offer investment opportunities through cash value accumulation.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Insurance
Choosing the right insurance coverage requires careful consideration of your individual needs and circumstances. Here are some key factors to consider:
-
Risk Assessment: Identify the risks you face and assess the potential financial impact of those risks.
-
Coverage Needs: Determine the appropriate amount of coverage you need to adequately protect yourself and your assets.
-
Policy Terms and Conditions: Carefully review the policy terms and conditions, including coverage limits, exclusions, deductibles, and premiums.
-
Insurance Company Reputation: Choose an insurance company with a strong financial rating and a good reputation for customer service.
-
Cost: Compare quotes from multiple insurance companies to find the best coverage at a competitive price.
-
Deductibles: A deductible is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. Higher deductibles usually mean lower premiums, but you’ll have to pay more if you file a claim. Choose a deductible that you can comfortably afford.
-
Exclusions: Understand what the policy doesn’t cover. Exclusions are specific events or circumstances that are not covered by the policy. For example, a homeowners policy might exclude flood damage.
-
Riders and Endorsements: These are additions to your policy that provide extra coverage for specific items or situations. For example, you might add a rider to your homeowners policy to cover valuable jewelry.
-
Independent Agent vs. Direct Writer: An independent insurance agent can provide quotes from multiple insurance companies, while a direct writer represents only one company. Working with an independent agent can help you compare options and find the best coverage for your needs.
The Future of Insurance
The insurance industry is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, changing demographics, and emerging risks. Some of the key trends shaping the future of insurance include:
-
Digitalization: Insurance companies are increasingly using digital technologies to improve customer service, streamline processes, and offer personalized products.
-
Data Analytics: Data analytics is being used to assess risk more accurately, detect fraud, and personalize pricing.
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is being used to automate tasks, improve claims processing, and provide personalized advice.
-
Internet of Things (IoT): IoT devices, such as smart home sensors and wearable health trackers, are providing insurers with new data to assess risk and offer tailored coverage.
-
Climate Change: Climate change is increasing the frequency and severity of natural disasters, posing new challenges for the insurance industry.
-
Cybersecurity: Cyberattacks are becoming more sophisticated and frequent, creating a growing need for cyber insurance.
Conclusion
Insurance is an essential tool for managing risk and protecting yourself, your family, and your business from financial losses. By understanding the principles of insurance, the different types of coverage available, and the factors to consider when choosing a policy, you can make informed decisions and ensure that you have the right protection in place. The insurance landscape is constantly changing, so it’s important to stay informed about new trends and developments to ensure that your coverage remains adequate and relevant. Taking the time to properly assess your risks and choose the right insurance policies can provide peace of mind and financial security for years to come.